📙3️⃣ Practical Visualization Examples#
This notebook presents hands-on examples that build on the concepts introduced in earlier chapters. It is intended as a practical reference, offering reusable code snippets and templates that you can adapt for your own projects. Use this resource to deepen your understanding and to develop reproducible, high-quality visualizations.
You can also follow along with an interactive workshop notebook viewer supported by Neurodesk from the link below:

Fig. 39 Link to Neurodesk environment:#
Notebook Preparations#
Before diving into the visualization scripts, run the following (collapsed) setup cells to:
Connect to Google Colab (if applicable)
Import all necessary packages
Configure the required directory structure
Learn about the data used in these examples
Once these steps are complete, you’ll be ready to begin running the visualization workflows.
Click to expand section
Google Colab#
This chapter is designed to be fully interactive and can be run directly in a Google Colab environment. This allows you to experiment with the provided scripts, modify parameters, and explore how different choices affect the resulting visualizations.
To open this notebook in Colab, use the link below:
If you’re running this notebook in Colab, be sure to execute the cell below to install all required dependencies.
%%bash
# clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/sina-mansour/ohbm2025-reproducible-research.git
# install requirements
cd "ohbm2025-reproducible-research"
pip install -r requirements.txt
import os
# change to notebook directory
os.chdir("ohbm2025-reproducible-research/ohbm2025-reproducible-research/chapters/03/")
Package Imports#
The cell below imports all the packages required to run this notebook. It assumes that the necessary dependencies listed in requirements.txt have already been installed.
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import sparse
import colorcet as cc
import contextlib
from io import StringIO
import nibabel as nib
import json
# Cerebro brain viewer
from cerebro import cerebro_brain_utils as cbu
from cerebro import cerebro_brain_viewer as cbv
Directory Setup#
Next, let’s set up the directory structure that will be used throughout this tutorial. In this case, we’ll simply change into the appropriate directory, as the required data is already included as part of this repository.
# Initialize the working directory
working_directory = os.getcwd()
# create a flag to indicate whether the directory setup is complete
if 'directory_setup_complete' not in globals():
directory_setup_complete = False
# only proceed if the directory setup is not complete
if not directory_setup_complete:
# change the working directory to the home directory of the repository
os.chdir("../../..")
# print the current working directory to make sure it is correct
working_directory = os.getcwd()
print(f"Current working directory: {working_directory}")
# set the flag to indicate that the directory setup is complete
directory_setup_complete = True
else:
# print a message indicating that the directory setup is already complete
print("Directory setup is already complete. No changes made.")
print(f"Current working directory: {working_directory}")
Current working directory: /home/runner/work/ohbm2025-reproducible-research/ohbm2025-reproducible-research
Tutorial Data#
A minimal set of neuroimaging files has been prepared to support the execution of the examples in this notebook.
⚠️ Note: This curated data is provided exclusively for educational purposes as part of this Jupyter Book tutorial.
For access to complete datasets or for use beyond this tutorial, please refer to the original data sources listed below.
Data Sources#
The neuroimaging data used in this tutorial are derived from the following publicly available resources:
Human Connectome Project’s Group Average Adult Template (see Glasser et al.[1], Van Essen et al.[2], and Marcus et al.[3])
The Glasser Cortical brain atlas (see Glasser et al.[4])
Tractography data from the ORG fiber clustering atlas (see Zhang et al.[5])
Functional connectivity data from Mansour et al.[6] (more information)
Melbourne subcortical atlas (see Tian et al.[7])
Reproducible NeuroImaging Visualizations#
With the directory structure in place and example neuroimaging data made available, we can now turn our attention to creating a variety of code-based visualizations.
These examples are designed to illustrate best practices for reproducible neuroimaging visualization workflows and demonstrate how to effectively explore and present brain imaging data using code.
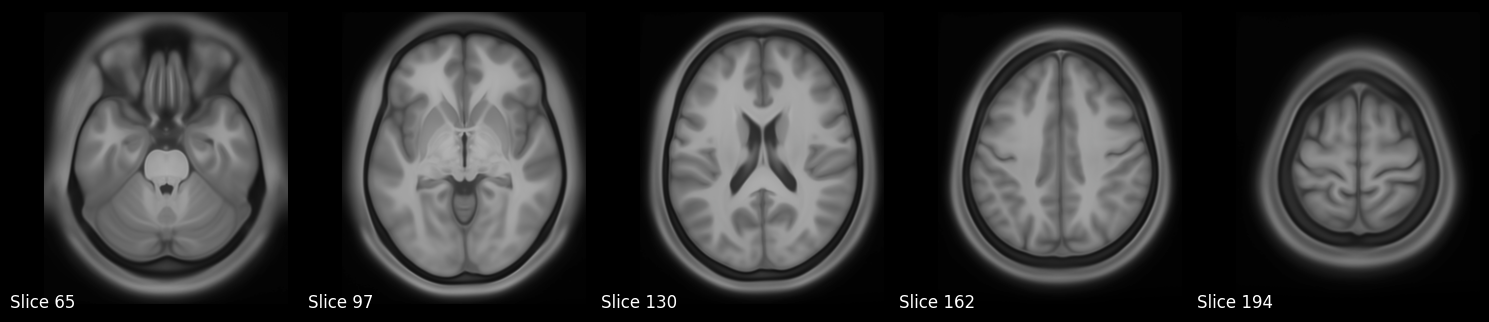
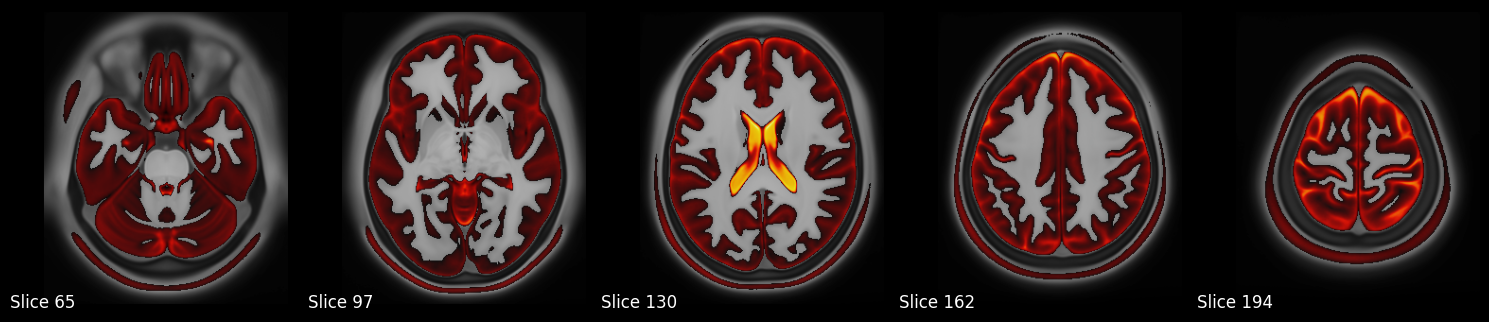
Volume Slice Rendering#
In this section, we’ll demonstrate how to render volume slices using data from the Human Connectome Project’s S1200 Group Average Data Release. Specifically, we’ll visualize a set of axial slices from the group-average T1-weighted image, followed by an overlay of the T2-weighted image using an arbitrary intensity threshold.
The images will be loaded using Nibabel, and slices will be visualized using Matplotlib. To promote reusability and reproducibility, we’ll structure the code as modular, well-documented functions.
visualize_multiple_axial_slices(f"{working_directory}/data/S1200_AverageT1w_restore.nii.gz")
# Visualize T1 weighted image, and overlay T2w on top of it
visualize_multiple_axial_slices_with_overlay(
f"{working_directory}/data/S1200_AverageT1w_restore.nii.gz",
f"{working_directory}/data/S1200_AverageT2w_restore.nii.gz"
)
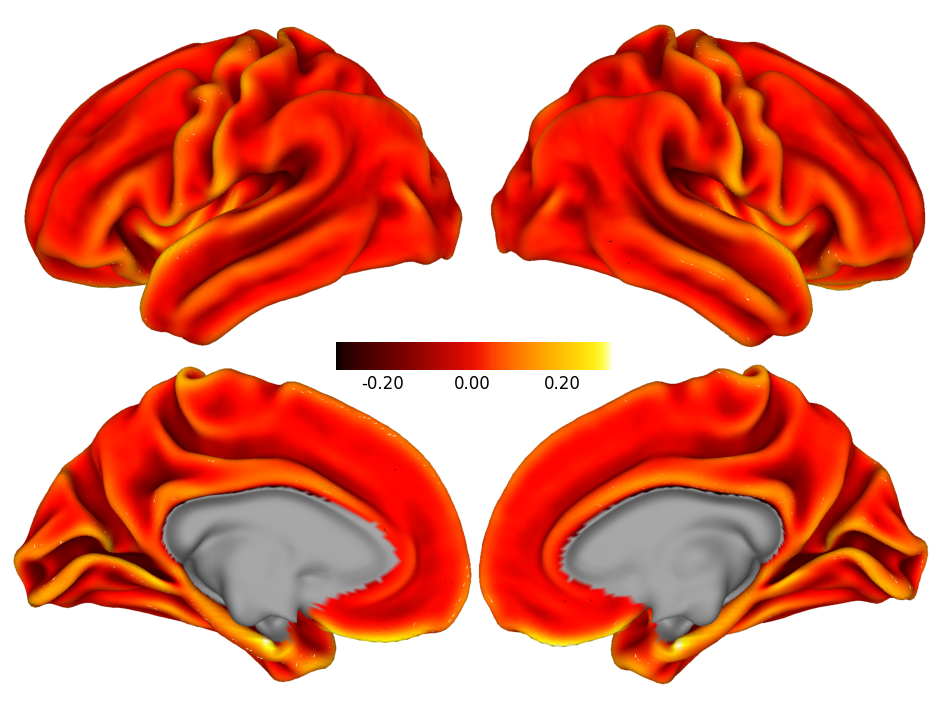
Surface-based Visualizations#
In the examples below, we will work with surface-based data from the Human Connectome Project’s S1200 Group Average Data Release, specifically using the fsLR template surface coordinates.
We’ll visualize the average cortical curvature mapped onto the cortical surface to highlight anatomical landmarks and folding patterns.
# Plot curvature dscalar file in gray scale
dscalar_file = f"{working_directory}/data/S1200.curvature_MSMAll.32k_fs_LR.dscalar.nii"
# Create a figure and axis for the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 9))
# Plot the dscalar file with Cerebro
plot_dscalar_with_cerebro(dscalar_file, fig=fig, ax=ax, colormap=cc.cm.fire, show_colorbar=True, colorbar_format='%.2f')
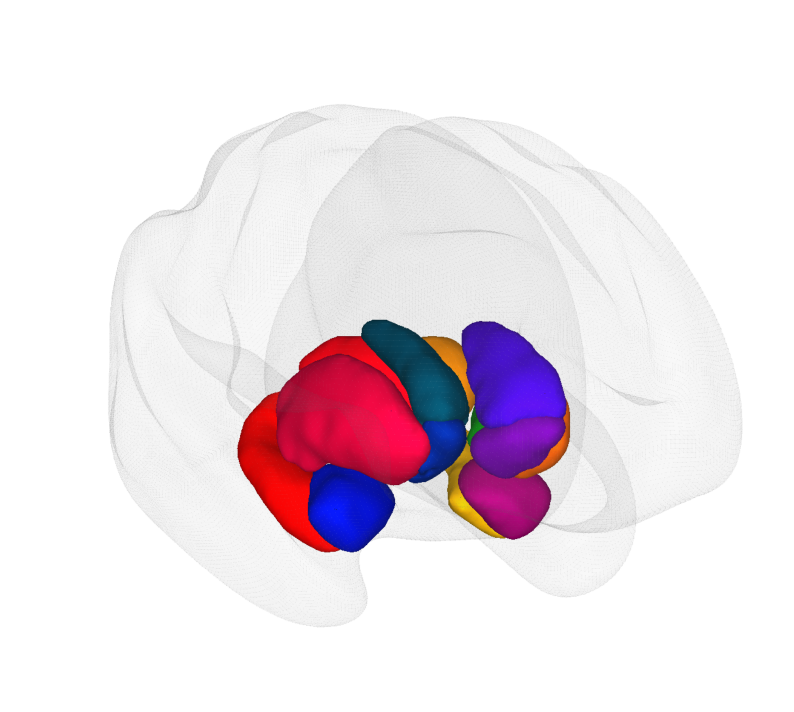
Volume-to-Surface Transformation#
In this example, we demonstrate how to perform a volume-to-surface transformation using the Melbourne Subcortical Atlas, specifically from its Scale 1 parcellation (available from Tian_Subcortex_S1_3T.nii.gz).
We will generate and render a separate cortical surface visualization for each labeled region in the atlas.
This transformation and rendering will be performed using tools from the Cerebro Brain Viewer, which provides convenient functionality for mapping volumetric data onto surface meshes.
# Create a figure and axis for the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 9))
# Suppress low-level output
old_stdout, old_stderr = suppress_c_output()
try:
# Plot the glass brain with the subcortical atlas
plot_glass_brain_and_atlas_with_cerebro(
ax=ax, atlas_file="data/Tian_Subcortex_S1_3T.nii.gz", view=((250, 350, 0), None, None, None), surface='inflated', glass_color=(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 0.2)
)
finally:
# Restore the original stdout and stderr
restore_c_output(old_stdout, old_stderr)
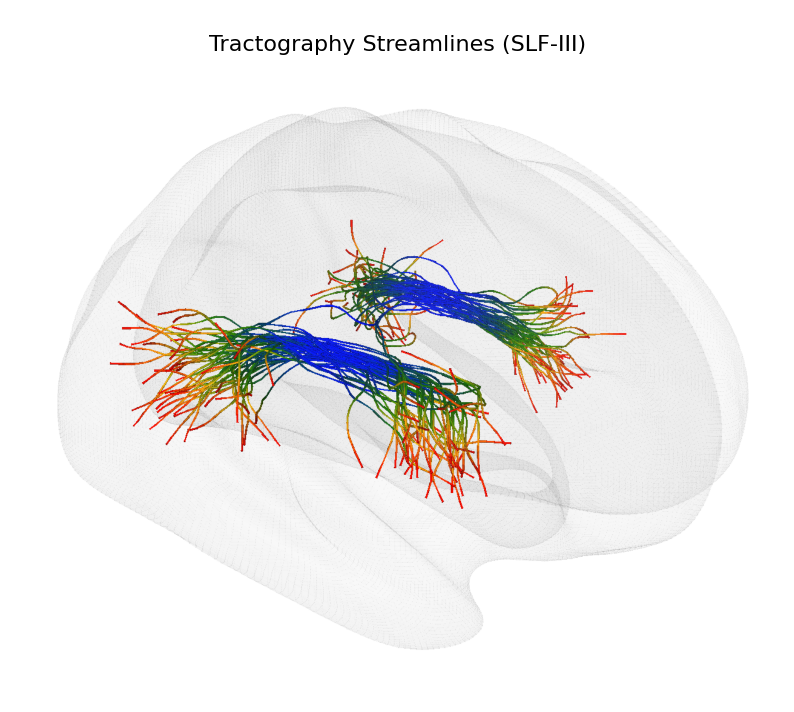
Tractography Visualization#
In this section, we will visualize tractography data from the ORG fiber clustering atlas. We will render a single fiber bundle using the Cerebro Brain Viewer, showcasing how to load and display streamline data effectively.
# Create a figure and axis for the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 9))
# Suppress low-level output
old_stdout, old_stderr = suppress_c_output()
try:
# Plot the glass brain with the subcortical atlas
plot_glass_brain_and_tractography_with_cerebro(
ax=ax, # axis to render the brain view on
tract_file="data/T_SLF-III-cluster_00209.tck", # path to the tractography file
view=((400, 150, 100), None, None, None), # camera view configuration for the brain viewer (a view from the right side, slightly tilted towards the frontal superior part of the brain)
surface='inflated', glass_color=(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 0.2)
)
finally:
# Restore the original stdout and stderr
restore_c_output(old_stdout, old_stderr)
# Add text to the plot
ax.text(0.5, 0.95, "Tractography Streamlines (SLF-III)", transform=ax.transAxes, fontsize=16, ha='center', va='center', color='black')
Text(0.5, 0.95, 'Tractography Streamlines (SLF-III)')
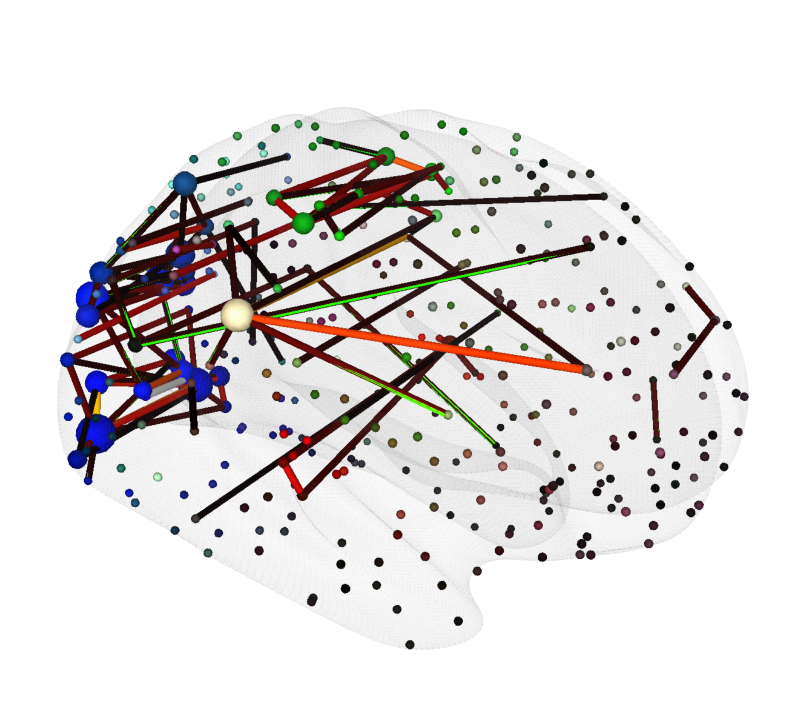
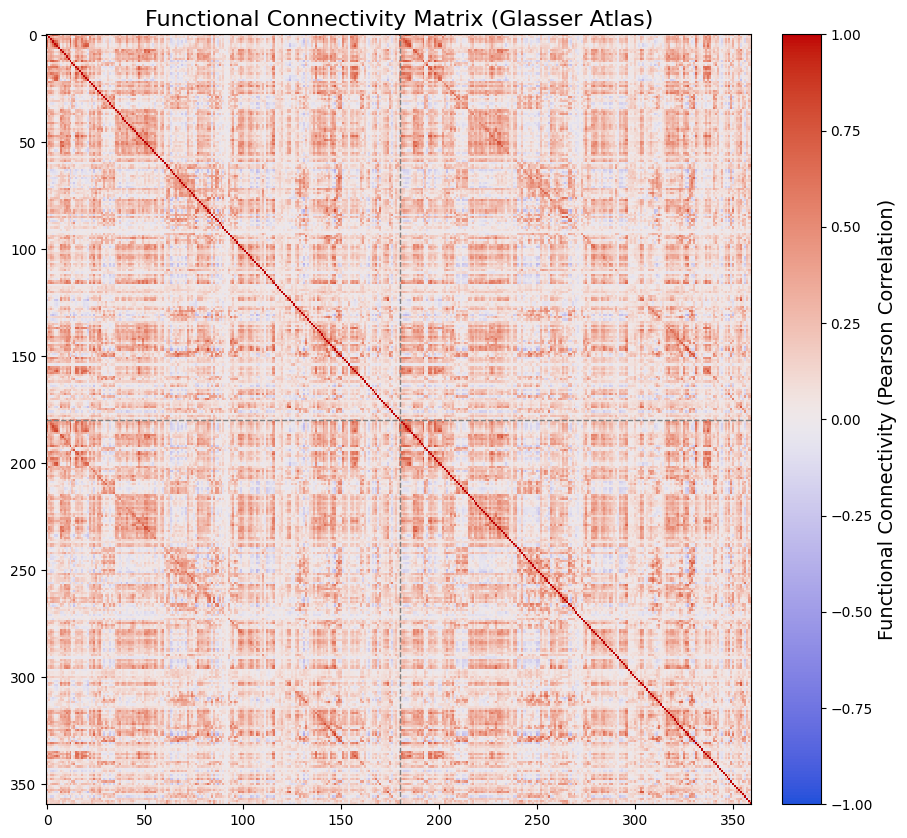
Brain Network Visualizations#
This example uses functional human connectome data from Mansour et al.[6]. We will visualize both a connectivity heatmap and a 3D brain network derived from an individual’s functional connectome, mapped onto the HCP MMP1 atlas (Glasser et al.[4]).
The connectivity heatmap will be created using Matplotlib, while the 3D brain network visualization will be generated with the Cerebro Brain Viewer.
# Get a figure and axis for the heatmap
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
# Plot the heatmap of the functional connectivity matrix
im = ax.imshow(fc_matrix_reordered, cmap=cc.cm.coolwarm, aspect='auto', interpolation='nearest', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
# Set the ticks and labels for the heatmap
glasser_label_names = [glasser_atlas_labels_dict[x][0] for x in range(1, max(glasser_atlas_labels_dict.keys()) + 1)]
# Add a dashed line at the middle of the heatmap to separate left and right hemispheres
ax.axvline(x=len(glasser_label_names)//2, color='gray', linestyle='--', linewidth=1)
ax.axhline(y=len(glasser_label_names)//2, color='gray', linestyle='--', linewidth=1)
# Add a colorbar to the heatmap
cbar = fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax, orientation='vertical', fraction=0.05, pad=0.04)
cbar.set_label('Functional Connectivity (Pearson Correlation)', fontsize=14)
# Set the title for the heatmap
ax.set_title("Functional Connectivity Matrix (Glasser Atlas)", fontsize=16)
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Functional Connectivity Matrix (Glasser Atlas)')
# Now that we have the functional connectivity matrix,
# we need the coordinates of the nodes in the glasser atlas
node_coords = np.array([lrxyz[surface_mask][glasser_atlas.get_fdata()[0] == x].mean(axis=0) for x in range(1, max(glasser_atlas_labels_dict.keys())+1)])
# Let's also extract node colors from the glasser atlas
glasser_label_colors = [glasser_atlas_labels_dict[x][1] for x in range(1, max(glasser_atlas_labels_dict.keys()) + 1)]
# Now let's threshold the functional connectivity matrix to only keep the strongest connections
threshold = 0.7 # threshold for the functional connectivity matrix
fc_matrix_thresholded = np.where(np.abs(fc_matrix_reordered) > threshold, fc_matrix_reordered, 0)
# also remove self-connections
np.fill_diagonal(fc_matrix_thresholded, 0)
# Node sizes can be set based on the degree of each node
node_degrees = np.sum(np.abs(fc_matrix_thresholded), axis=1)
node_radii = np.clip(node_degrees / np.max(node_degrees) * 5, 1, 5) # Scale node sizes between 1 and 5
node_radii = np.repeat(node_radii[:, np.newaxis], 3, axis=1) # Make node radii along 3 dimensions (N x 3)
# Edge radii can be set based on the strength of the connections
edge_radii = np.clip(np.abs(fc_matrix_thresholded) / np.max(np.abs(fc_matrix_thresholded)), 0.2, 1) # Scale edge sizes between 0.2 and 1
# Create a figure and axis for the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 9))
# Suppress low-level output
old_stdout, old_stderr = suppress_c_output()
try:
# Plot the glass brain with the subcortical atlas
plot_glass_brain_and_network_with_cerebro(
ax=ax, # axis to render the brain view on
adjacency_matrix=fc_matrix_thresholded, # The adjacency matrix of the network
node_coords=node_coords, # The coordinates of the nodes in the network
node_colors=glasser_label_colors, # The colors of the nodes in the network
node_radii=node_radii, # The radii of the nodes in the network
edge_radii=edge_radii, # The radii of the edges in the network
view=((400, 150, 100), None, None, None), # camera view configuration for the brain viewer (a view from the right side, slightly tilted towards the frontal superior part of the brain)
surface='inflated', glass_color=(0.9, 0.9, 0.9, 0.2)
)
finally:
# Restore the original stdout and stderr
restore_c_output(old_stdout, old_stderr)
(206,) (206, 2) (206, 4)